
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Center of Laser Fusion, Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
2 Science and Technology on Plasma Physics Laboratory, Mianyang 621900, China
3 IFSA Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Beryllium carbide (Be2C) thin films have proven to be promising ablation materials, but the properties of Be2C coatings of the greater thickness required for inertial confinement fusion capsules are still unknown. In this work, Be2C coatings of various thicknesses (0.3–32.9 μm) are prepared by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. The influence of thickness on crystal properties, microstructure, and optical properties is investigated. The results indicate that the crystallinity of polycrystalline Be2C films improves with increasing thickness, while the grain size (~5 nm) and texture properties (without a preferred orientation) have only a weak dependence on thickness. A uniform featureless microstructure and smooth surface (root mean square roughness ~8 nm) are observed even in thick (32.9 μm) films, despite the presence of defects induced by contaminants. High densities (2.19–2.31 g/cm3) and high deposition rates (~270 nm/h) are realized, with the latter corresponding to the upper limit for the fabrication of Be2C coatings by magnetron sputtering. The transmittance of the films in the near-infrared region remains at a high level (>80%) and has only a weak dependence on thickness, while the transmittance in the visible region decreases with increasing thickness. In addition, the optical bandgap is estimated to be about 1.9 eV and decreases with increasing thickness owing to the presence of defects.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2019, 4(4): 045403
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang621900, China
2 Science and Technology on Plasma Physics Laboratory, Mianyang621900, China
The Be-based materials with many particular properties lead to an important research subject. The investigation progresses in the fabrication technologies are introduced here, including main three kinds of Be-based materials, such as Be–Cu capsule, $\text{Be}_{2}\text{C}$ ablator and high-purity Be material. Compared with the pioneer workgroup on Be-based materials, the differences in Be–Cu target fabrication were described, and a grain refinement technique by an active hydrogen reaction for Be coating was proposed uniquely. $\text{Be}_{2}\text{C}$ coatings were first prepared by the DC reactive magnetron sputtering with a high deposition rate $({\sim}300~\text{nm}/\text{h})$. Pure polycrystalline $\text{Be}_{2}\text{C}$ films with uniform microstructures, smooth surface, high density $({\sim}2.2~\text{g}\cdot \text{cm}^{3})$ and good optical transparency were fabricated. In addition, the high-purity Be materials with metal impurities in a ppm magnitude were fabricated by the pyrolysis of organometallic Be.
Be-based materials Be–Cu capsule Be2C ablator high purity High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(2): 02000e10
1 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 等离子体物理重点实验室, 四川 绵阳 621900
可控核聚变反应是科学家用来解决能源缺乏和发展可持续能源的理想途径,为此美国开展了惯性约束聚变(ICF)研究,建设了国家点火装置(NIF),旨在实验室演示核聚变反应,为惯性约束聚变能(IFE)发展指明方向。制靶是NIF点火工程三大主体之一,如何制备满足设计需求的靶丸成为科学家不懈努力的追求目标。详细介绍了NIF工程中主要候选Be靶丸需求背景、研究现状、Be靶优势、靶参数设计要点、靶丸制备技术,以及制靶过程中存在的关键技术问题,为我国Be靶制备及制靶能力建设提供参考信息。
惯性约束聚变 铍靶丸 靶参数 inertial confinement fusion beryllium target target parameter National Ignition Facility NIF 强激光与粒子束
2013, 25(12): 3259
1 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 中国工程物理研究院 等离子体物理重点实验室, 四川 绵阳 621900
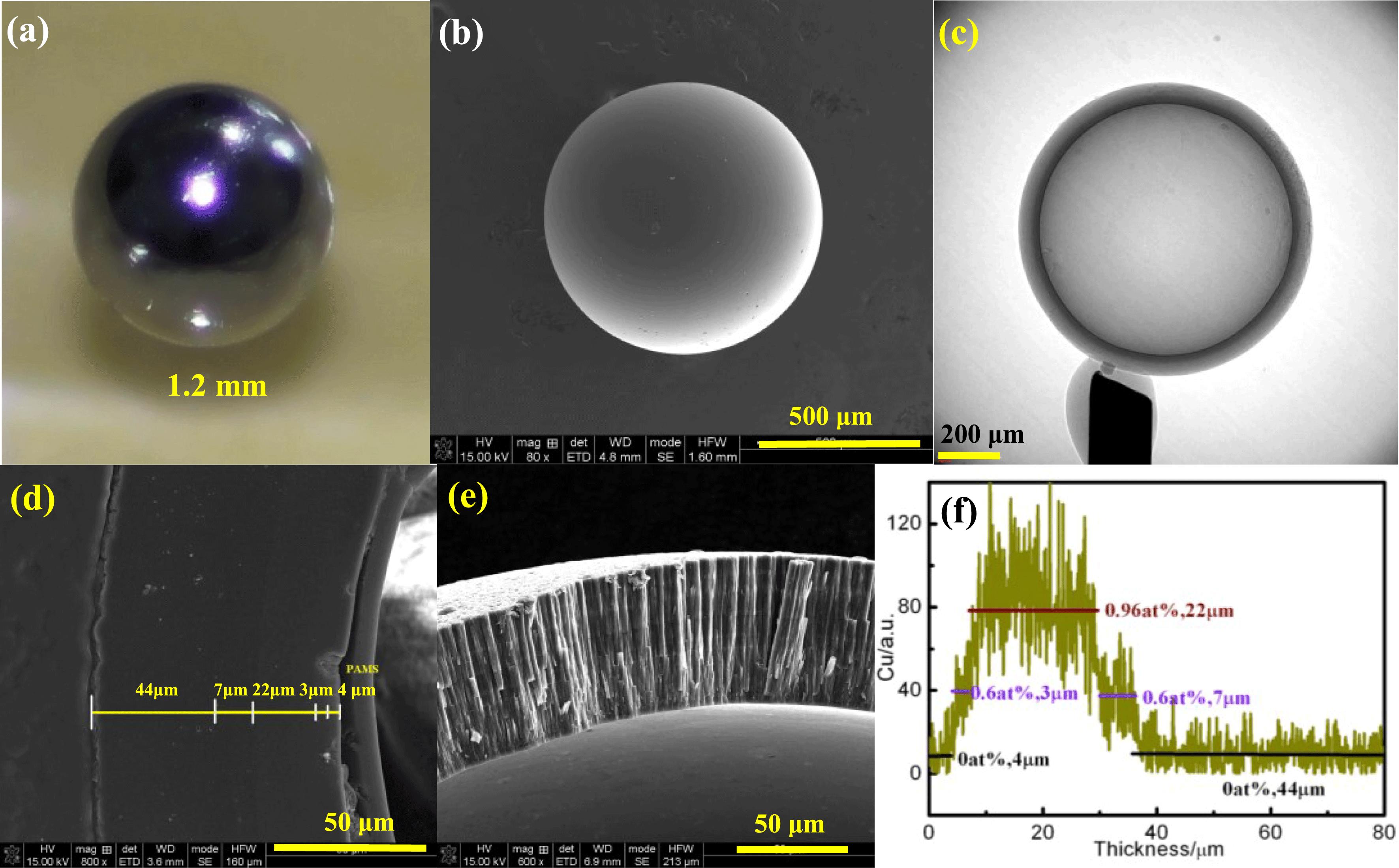
采用腐蚀去合金化方法制备纳米多孔铜材料。研究了固溶时间、腐蚀时间及腐蚀温度对纳米多孔铜表面形貌及残余Mn含量的影响。研究表明:由于固溶时间的延长,合金成分越来越均匀化,去合金化后所得纳米多孔铜的残余Mn原子分数降低。固溶95 h的前驱体合金,随着腐蚀时间的延长,其残余Mn含量降低不明显;随着温度的升高,其残余Mn原子分数由25 ℃的3.54%降至60℃的1.14%,但是60 ℃腐蚀后的孔隙与丝径尺寸明显粗化,样品易碎。通过调整去合金化参数,实验所制备的纳米多孔铜呈现均匀的海绵状纳米多孔结构,残余Mn原子分数1.23%,平均丝径尺寸40 nm。
纳米多孔铜 去合金化 前驱体合金 表面形貌 nanoporous copper dealloying precursor alloy surface morphology
中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
采用蒸发铍原子与非平衡态氢原子反应制备了透明的BeH2薄膜。扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察到薄膜表面存在微孔洞, 红外光谱显示在722 cm-1有一个强烈的吸收峰。采用密度泛函理论(DFT)对BeH2网状结构进行了计算, 得到的3个基本振动模式的频率和强度与文献中BeH2粉末的实验数据基本一致, 其中弯曲振动的计算频率为747 cm-1, 与BeH2薄膜的红外吸收峰一致。推测BeH2薄膜的结构与BeH2粉末有所不同, 因而导致某些振动峰被抑制。
BeH2薄膜 红外光谱 振动模式 密度泛函理论 BeH2 films infrared spectra vibration modes density functional theory





